Business Process Automation: A Complete Guide & Benefits
Learn what business process automation is, see real examples, and discover the benefits that boost efficiency and significantly cut costs for your business.
What We Will Learn
By the end of this guide, you'll be able to:
- Understand what business process automation is and how it transforms operations
- Identify which processes in your business are ready for automation
- Discover real-world examples of BPA across different departments
- Learn the key benefits that deliver measurable ROI
- Implement automation successfully with proven strategies
- Avoid common pitfalls that derail automation projects
Understanding Business Process Automation
Business process automation (BPA) represents the technology-enabled transformation of repetitive, manual tasks into streamlined, automated workflows. At its core, BPA uses software to execute recurring business processes with minimal human intervention, allowing organizations to operate more efficiently and focus human talent on strategic, high-value activities.
According to McKinsey, 66% of businesses have automated at least one business process as of 2024, demonstrating widespread adoption across industries. The market itself reflects this momentum—the global BPA market is projected to grow from $13 billion in 2024 to $23.9 billion by 2029, representing a compound annual growth rate of 11.6%.
"Automation is not about replacing people; it's about amplifying their capabilities and freeing them to do what humans do best—innovate, create, and solve complex problems."
Manual vs. Automated Workflow Comparison
| Stage | Manual Process | Automated Process |
| Step 1 | Employee receives invoice via email | System automatically captures invoice |
| Step 2 | Manual data entry into accounting system | OCR extracts data automatically |
| Step 3 | Search for matching purchase order | System matches PO instantly |
| Step 4 | Email supervisor for approval | Auto-routes to approver based on rules |
| Step 5 | Wait for email response | Instant approval notification |
| Step 6 | Manually schedule payment | Payment scheduled automatically |
| Time Required | 15-30 minutes per invoice | 2-3 minutes per invoice |
| Error Rate | 3-5% (human error) | <0.1% (system error) |
When you automate business processes, you're essentially creating digital workflows that handle routine operations such as data entry, invoice processing, customer communications, and report generation. These automated systems follow predefined rules and logic to complete tasks that would otherwise consume significant employee time and introduce the potential for human error.
The scope of business automation extends far beyond simple task completion. Modern business process automation software integrates with existing systems, pulls data from multiple sources, triggers actions based on specific conditions, and maintains comprehensive audit trails of all activities. This interconnected approach ensures that automating business processes doesn't create isolated efficiency gains but rather transforms entire operational ecosystems.
Types of Business Process Automation
Business automation manifests in various forms, each addressing different organizational needs and complexity levels.
BPA Types Comparison
| Type | Complexity Level | Best For | Common Use Cases | Implementation Time |
| Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Low to Medium | Rule-based, repetitive tasks | Data entry, invoice processing, system integration | 2-4 weeks |
| Workflow Automation | Medium | Multi-step processes with approvals | Employee onboarding, purchase approvals, content publishing | 4-8 weeks |
| Intelligent Automation | High | Complex decision-making | Document processing, customer service routing, predictive maintenance | 8-16 weeks |
| Integration Automation | Medium to High | Cross-platform data sync | CRM updates, inventory management, multi-system workflows | 4-12 weeks |
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) uses software robots to mimic human actions within digital systems. These bots can log into applications, move files, extract data, fill in forms, and perform calculations. RPA excels at automating rule-based tasks that don't require complex decision-making, making it ideal for data entry, invoice processing, and system integration tasks.
Workflow Automation orchestrates multi-step processes involving multiple stakeholders and systems. This type of automation ensures that tasks move seamlessly from one person or department to another based on predefined rules. Examples include employee onboarding workflows, purchase approval processes, and content publishing pipelines.
Intelligent Business Process Automation combines traditional BPA with artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities. This advanced form can handle unstructured data, make decisions based on patterns, and continuously improve through experience. Intelligent automation excels at document processing, customer service routing, and predictive maintenance scheduling.
Integration-Based Automation connects different software applications to enable seamless data flow without manual intervention. When one system updates, the changes automatically propagate to connected platforms, eliminating duplicate data entry and ensuring consistency across your technology stack.
Real-World Business Process Automation Examples
Understanding how organizations implement BPA across different functions helps illustrate its versatility and impact.
Customer Service Ticket Automation: Before & After
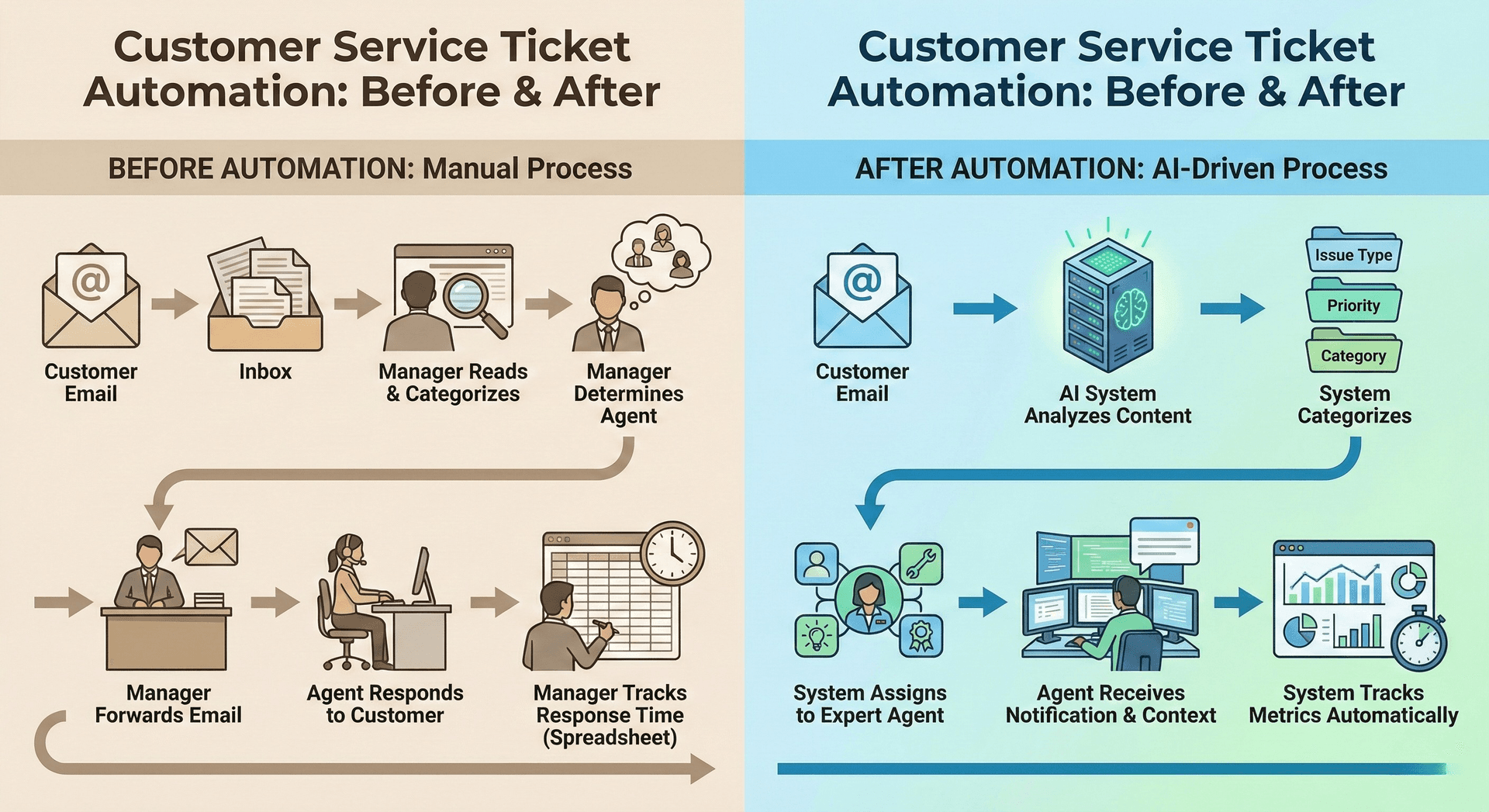
Before Automation:
- 1Customer sends an email to the support inbox
- 2Support manager manually reads and categorizes emails
- 3The manager determines which agent has relevant expertise
- 4Manager forwards email to agent
- 5The agent responds to the customer
- 6Manager manually tracks response time in a spreadsheet
Total Time: 45-60 minutes average response time | Manual Effort: 15-20 minutes per ticket
After Automation:
- 1Customer sends an email to the support inbox
- 2The system analyzes email content using AI
- 3System categorizes by issue type and priority
- 4The system assigns to an available agent with matching expertise
- 5The agent receives a notification with the customer context
- 6System tracks all metrics automatically
Total Time: 5-10 minutes average response time | Manual Effort: 0 minutes (fully automated routing)
Finance and Accounting
Financial departments automate invoice processing by extracting data from incoming invoices, matching them with purchase orders, routing for approval, and scheduling payments—all without manual data entry. The impact is significant: 83% of organizations using AP automation report reduced payment friction through better payment integration between buyers and suppliers, while automated processing speed has reduced invoicing errors for 77% of firms.
Expense report management becomes streamlined when employees submit receipts through mobile apps, automated systems verify policy compliance, flag exceptions, and process reimbursements within predefined timeframes.
Human Resources
HR teams leverage business automation to transform employee onboarding. Automated workflows send welcome emails, create accounts across multiple systems, assign training modules, schedule orientation sessions, and collect necessary documentation. Performance review cycles become manageable through automated reminder systems that notify managers of deadlines, collect feedback from multiple sources, and compile comprehensive review packages.
Sales and Marketing
Sales teams automate lead nurturing campaigns that send personalized emails based on prospect behavior, score leads according to engagement metrics, and alert sales representatives when prospects reach threshold scores. Marketing departments use automation to schedule social media posts, segment audiences based on behavior, trigger targeted campaigns, and generate performance reports.
Customer Service
Support teams implement automated ticket routing that analyzes incoming requests, categorizes them by issue type, assigns them to appropriate agents based on expertise and workload, and escalates unresolved issues according to service level agreements. Chatbots handle routine customer inquiries, provide instant responses to common questions, collect necessary information before human handoff, and operate around the clock without breaks.
Operations Management
Operations teams automate inventory management systems that track stock levels in real-time, generate purchase orders when quantities fall below thresholds, coordinate with suppliers, and update accounting systems. Supply chain automation monitors shipments, predicts delays based on historical data, reroutes deliveries when necessary, and keeps stakeholders informed throughout the process.
Key Business Process Automation Benefits
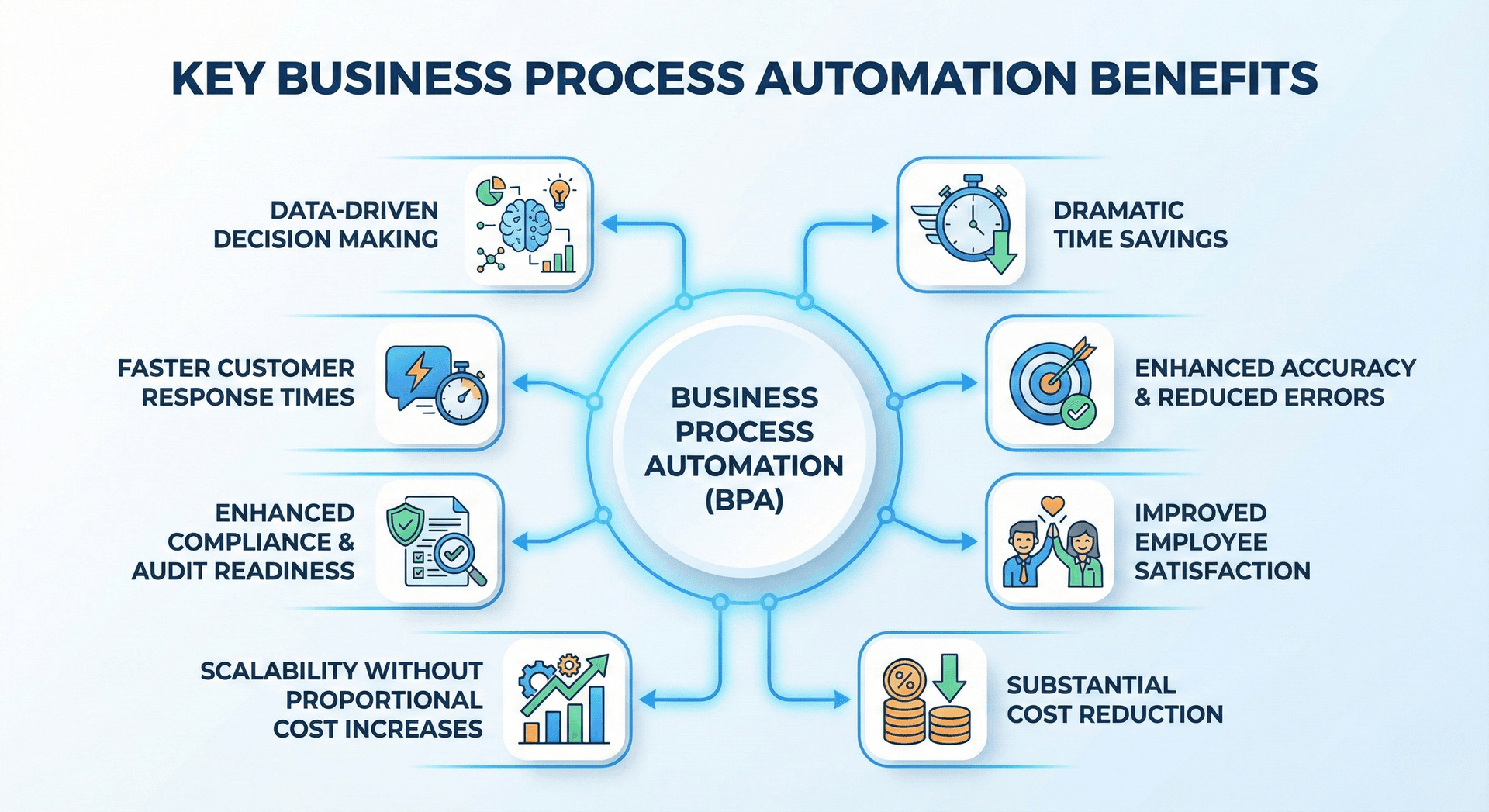
Organizations that embrace BPA experience transformative advantages across operational, financial, and strategic dimensions.
Dramatic Time Savings emerge as the most immediate benefit. Automating business processes eliminates the time employees spend on repetitive tasks. What once required hours of manual effort can be completed in minutes or seconds. In fact, 73% of IT leaders report that automation saves 10-50% of the time previously spent on manual tasks. This time reclamation allows teams to redirect their energy toward innovation, customer relationships, and strategic initiatives that drive business growth.
Enhanced Accuracy and Reduced Errors represent critical operational improvements. Human error rates in manual data entry typically range from 1% to 4%, depending on task complexity. Automated systems execute tasks with near-perfect accuracy, following programmed logic without fatigue or distraction. This reliability proves especially valuable in compliance-sensitive industries where errors carry significant consequences.
Improved Employee Satisfaction often surprises organizations exploring automation. Rather than fearing job loss, employees typically welcome liberation from monotonous tasks. Freed from repetitive work, team members engage in more meaningful activities that leverage their creativity, problem-solving abilities, and interpersonal skills. This shift increases job satisfaction and reduces turnover.
Substantial Cost Reduction occurs through multiple channels. Direct labor costs decrease when automation handles tasks previously requiring human hours. Error-related costs diminish as accuracy improves. Compliance costs decline when automated systems maintain perfect documentation and ensure adherence to regulations. Businesses using BPA report cost reductions between 10% and 50%, primarily by automating repetitive tasks and minimizing manual errors. Organizations typically see return on investment within months of implementing business process automation software, with some reporting ROI improvements ranging from 30% to 200% within the first year.
Scalability Without Proportional Cost Increases becomes achievable when core processes run on automated systems. Growing organizations traditionally need to hire additional staff proportionally to handle increased transaction volumes. Automated processes scale to handle 10x or 100x more volume with minimal additional cost, enabling growth without corresponding operational complexity.
Enhanced Compliance and Audit Readiness result from automation's inherent documentation capabilities. Every action, decision, and exception gets logged automatically, creating comprehensive audit trails. When regulators request documentation or internal audits occur, automated systems provide complete, organized records instantly rather than requiring weeks of manual compilation.
Faster Customer Response Times improve satisfaction and competitive positioning. Automated processes don't wait for business hours, approval chains, or employee availability. Customer requests receive immediate acknowledgment, routine inquiries get instant resolution, and complex issues are routed to appropriate specialists without delay.
Data-Driven Decision Making becomes more accessible when automated systems collect, organize, and analyze operational data. Business process automation software generates real-time dashboards showing process performance, identifies bottlenecks, highlights trends, and provides insights that inform strategic decisions.
How to Identify Processes for Automation
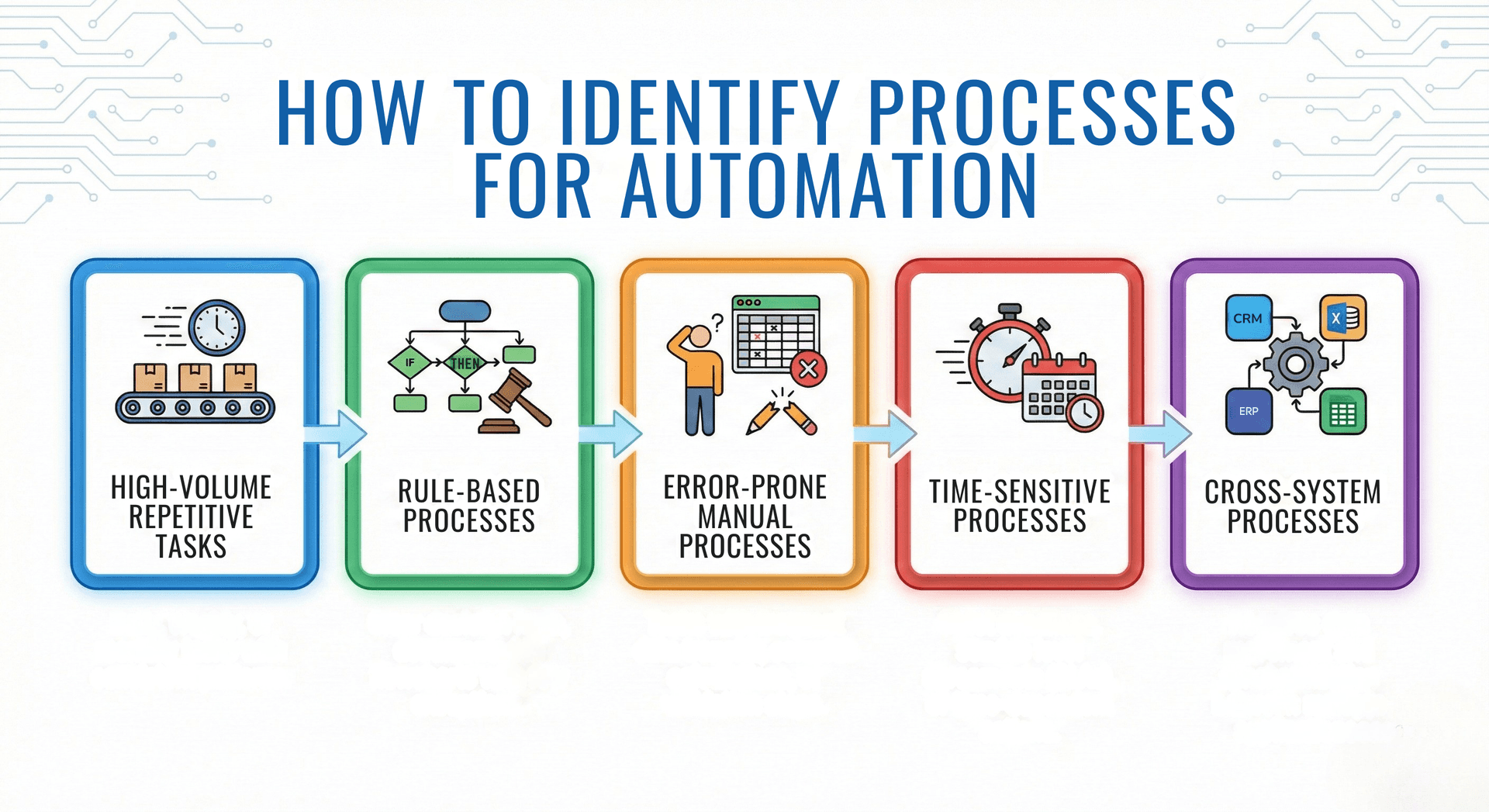
Not every process deserves automation. Strategic selection maximizes return on investment and ensures successful implementation.
High-Volume Repetitive Tasks represent ideal automation candidates. Processes that occur daily, weekly, or monthly with consistent patterns deliver significant time savings when automated. Calculate the total hours spent on a task annually to understand the potential impact. A task consuming 30 minutes daily consumes 120 hours annually—substantial time that automation could reclaim.
Rule-Based Processes with clear decision logic translate well to automation. If you can document the process in an if-then flowchart without excessive exceptions, automation will likely succeed. Processes requiring significant human judgment or handling highly variable situations may need intelligent automation or continued human oversight.
Error-Prone Manual Processes benefit tremendously from automation. Tasks involving data transfer between systems, complex calculations, or multiple validation steps often generate errors that cost time and money to correct. Automating these processes eliminates error sources while improving reliability.
Time-Sensitive Processes where delays create negative consequences deserve automation priority. Processes with strict deadlines, service level agreements, or time-dependent actions benefit from automation's consistency and speed.
Cross-System Processes requiring data movement between multiple applications create efficiency drains and error opportunities. Integration-based automation eliminates manual data transfer, ensures consistency, and accelerates process completion.
Start by mapping current workflows, documenting time requirements, identifying pain points, and calculating error rates. Engage employees who perform these tasks daily—they possess invaluable insights into friction points and automation opportunities. Prioritize processes based on impact potential, implementation complexity, and alignment with strategic objectives.
Implementing Business Process Automation Successfully
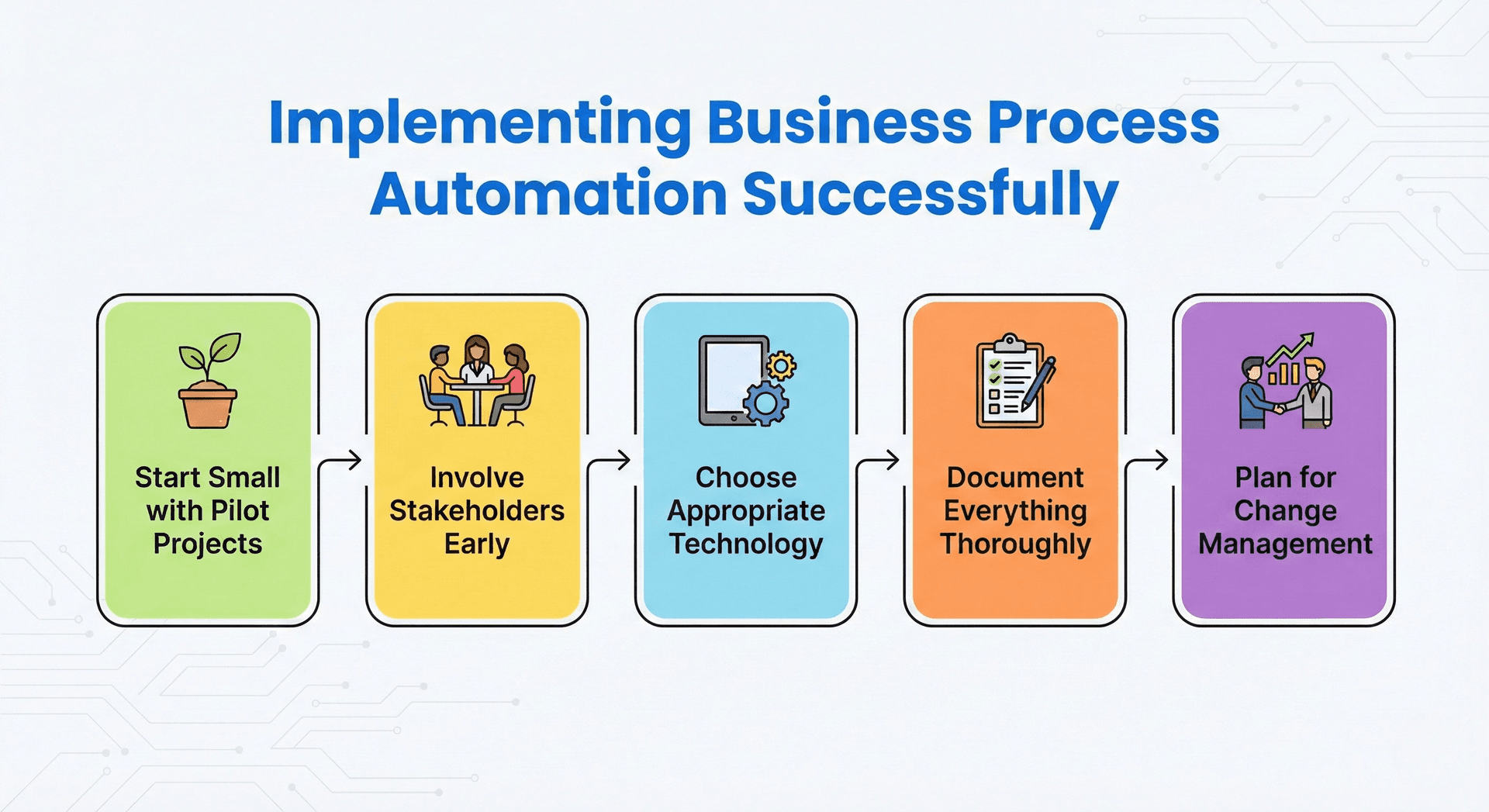
Successful BPA implementation requires strategic planning, stakeholder engagement, and continuous optimization.
Start Small with Pilot Projects rather than attempting enterprise-wide transformation immediately. Select one high-impact, manageable process for initial automation. This approach allows your team to learn, demonstrate value, build confidence, and establish best practices before scaling.
Involve Stakeholders Early in the automation journey. Employees who perform current processes understand nuances that documentation might miss. Their involvement ensures accurate workflow mapping, identifies potential issues before deployment, and builds support for change. Address concerns transparently and emphasize how automation enhances rather than replaces their roles.
Choose Appropriate Technology based on your specific needs, technical capabilities, and budget. Options range from no-code automation platforms suitable for business users to enterprise integration solutions requiring IT expertise. Consider factors including existing system compatibility, scalability requirements, vendor support quality, and total cost of ownership.
Document Everything Thoroughly before, during, and after implementation. Current state documentation establishes baseline metrics. Implementation documentation captures configuration decisions and business rules. Ongoing documentation maintains institutional knowledge as processes evolve. This documentation proves invaluable for troubleshooting, optimization, and compliance.
Monitor, Measure, and Optimize Continuously after deployment. Establish key performance indicators aligned with automation objectives. Track metrics including processing time, error rates, cost savings, and user satisfaction. Regular reviews identify optimization opportunities and ensure automated processes continue meeting business needs as conditions change.
Plan for Change Management throughout the implementation. Communicate clearly about automation goals, timeline, and impacts. Provide training on new systems and processes. Celebrate wins and address concerns promptly. Successful automation requires technology and organizational change working in harmony.
The Future of Business Process Automation
Business automation continues evolving rapidly, driven by advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing. AI adoption in business has surged dramatically from 55% in 2023 to 72% in 2024, with 74% of AI-using companies planning to increase their investment in the next three years. Intelligent business process automation increasingly handles complex scenarios that previously required human judgment.
Natural language processing enables systems to understand and respond to unstructured communications. Predictive analytics anticipate issues before they occur, triggering proactive responses. The emergence of hyperautomation—which combines AI, RPA, and other technologies—is expected to drive spending to nearly $600 billion in the mid-2020s.
The convergence of automation technologies creates unprecedented possibilities. Imagine systems that automatically identify inefficient processes, design optimal workflows, implement automation, and continuously refine operations based on performance data. This self-improving automation represents the trajectory of business technology.
Organizations that embrace business process automation position themselves for competitive advantage. They operate more efficiently, respond to customers faster, scale without proportional cost increases, and free human talent for innovation. Those that delay automation risk falling behind competitors who leverage these capabilities to deliver superior value at lower costs.
"The question is no longer whether to automate, but how quickly and strategically you can transform your operations to thrive in an increasingly automated business landscape."
Meet CronDesk: Your Unified Business Dashboard
While understanding business process automation is essential, implementing it effectively requires the right tools. CronDesk brings your scattered business operations into one unified command center, enabling you to manage payments, communications, tasks, and workflows from a single dashboard.
Instead of switching between Stripe for payments, Gmail for emails, Asana for tasks, and countless other tools, CronDesk lets you handle everything in one place. Process refunds, reply to customer emails, assign team tasks, approve invoices, and monitor your operations—all without leaving your dashboard. With real-time updates and quick action capabilities, you can respond to business events instantly and keep your operations running smoothly.
If you're exploring automation but want simplicity instead of complex enterprise tools, CronDesk offers a practical starting point for small businesses and growing teams alike.
Ready to Boost Your Digital Presence?
Get expert guidance from Soyayeb Hasan Shafin and transform your business with proven digital marketing strategies. Whether you need AI engine optimization, social media marketing, or comprehensive digital growth, we've got you covered.
FAQs
Related CronBoost Services
Take your digital marketing to the next level with these strategic services: